Ray Optics Or Geometrical Optics
Ray Optics or Geometrical Optics In this optics, the light is considered as a ray which travels in a straight line. It states that for each and every object, there is an image.
Reflection Reflection is the phenomenon of changing the path of light without any change in the medium.
Reflection of Light The returning back of light in the same medium from which it has come after striking a surface is called reflection of light.


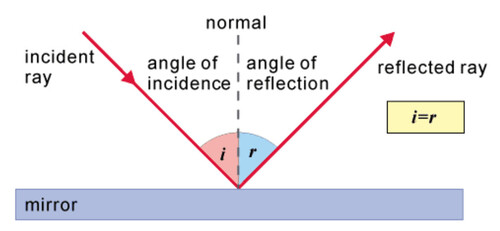
Laws Of Reflection Of Light
(a) The angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence
\(\angle i=\angle r\)
(b) The incident ray,relflected ray, and the normal to the reflection surface at the point of incidence lie in the same plane


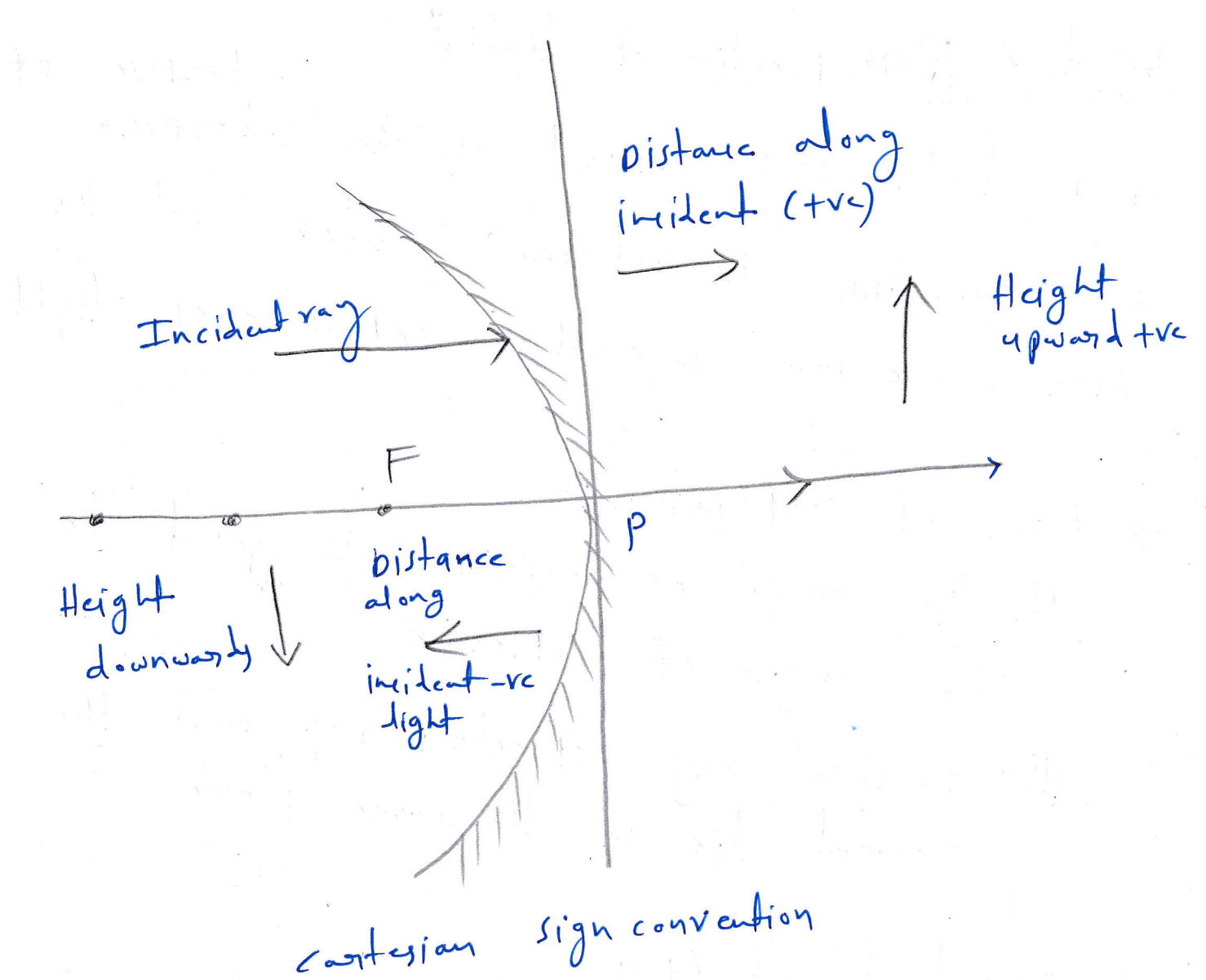
Cartesian Sign Convention
The cartesian sign convention for mirrors are
1.All the distances are to be measured from the pole of the mirror( or optical center of the lens)
2.The distances measured in the same direction as the incident light are taken as positive and those measured in the direction opposite to the direction of incident light are taken as negative
3.The height measured upwards with respect to the principal axis and normal to the principal axis are taken as positive. The height measured downward are taken as negative


The Mirror Equation
\(\frac {1} {v}+\frac 1 u=\frac 1 f\)
u = object distance
v = image distance
f = focal length
Linear Magnification =\(\frac {\text{Height of image }} {\text{Height of object}}\)
\(m=\frac {h_i} {h_0}=-\frac v u\)


Laws Of Refraction
(a) The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal to the interface at the point of incidence lie in the same plane
(b) Snell's law :
The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant
\(\frac {\sin i} {\sin r}=\mu_{21}\)
\(\mu_{21}\) is the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium


Principle Of Reversibility
Principle of reversibility of light states that when the final path of a ray of light after any number of reflections and refractions is reversed, the ray retraces its entire path.


Incidence Ray
Taking incidence ray BM and refracted ray MD
BN=CN-CB=OM-CB =a-R
\(MB=\sqrt{d^2+(a-R^2)}\)
\(\therefore\ \text{sin i}=\frac{BN}{BM}=\frac{(a-R)}{\sqrt{d^2+(a+R^2)}}\)
\(\angle \text{r}=\angle\text{a}=\angle AMN\)
Sin r=cos \((90^\circ-\alpha)=\frac{AN}{AM}=\frac{a+R}{\sqrt{d^2+(a+R)^2}}\)
For incidence ray BM to the horizontal level of liquid MP, MN will be normal at M. \(\angle\text{i}\) and \(\angle \text{r}\) will be incidence and refracted angles when ray BM passes from liquid ( \(\mu\)) to air. By Snell’s law, as ray passes from liquid to air
\(_1\mu_0=\frac{\text{sin i}}{\text{sin}\ \text{r}}\Rightarrow \frac{\mu_0}{\mu_1}=\frac{\text{sin i}}{\text{sin r}}[\mu_0\ \text{for air}=1][\mu_1=\mu\ \text{for liquid}]\)
\(\frac{1}{\mu_1}=\frac{\text{sin i}}{\text{sin r}}\)
\(\frac{1}{\mu_1}=\frac{\frac{a-R}{\sqrt{d^2+(a-R)^2}}}{\frac{(a+R)}{\sqrt{d^2+(a+R)^2}}}=\frac{(a-R)\sqrt{d^2+(a+R)^2}}{(a+R)\sqrt{d^2+(a-R)^2}}\)
\(d=\frac{\mu(a^2-d^2)}{\sqrt{(a+r)^2-\mu(a+r)^2}}\)
It is required expression.


Liquids Are Immiscible
The liquids are immiscible, so liquids arranged from bottom to top \(d_1,d_2\) and \(d_3\) with their refractive indices \(\mu_1,\mu_2,\mu_3\) respectively separated by layers \(l_1,l_2\) Consider the layer \(l_1\) . Let object is at its bottom at P then distance (\(\text{x}_1\) ) of image of P by liquid of refractive index \(\mu_1\) from layer \(l_1.\)
\(x_1=\frac{h/3}{_2\mu_1}\because\ _2\mu_1=\frac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}\)
\(\therefore\ x_1=\frac{h}{3\frac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}}=\frac{h}{3}\frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}\)
This image \(I_1\) acts as object for liquid of \(\mu_2\) and form the image at \(I_2\) .
The distance \(\text{x}_2\) below level \(l_2\).
Real depth \(=\Big(\frac{h}{2}+\text{x}_1\Big)\)
\(x_2=\frac{Real \ \ debth}{_3\mu_2}=\frac{Real\ \ depth }{\mu_2/\mu_3}\)
\(x_2=\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_2}\Big[\frac{h}{3}+x_1\Big]=\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_2}\Big[\frac{h}{3}+\frac{h}{3}\frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}\Big]=\frac{h}{3}\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_2}\Big[1+\frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}\Big]\)
\(=\frac{h}{3}\Big[\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_2}+\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_2}\frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}\Big]=\frac{h}{3}\Big[\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_2}+\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_1}\Big]\)
As the point P is seen from outside
\(x_3=\frac{\mu_0}{\mu_3}\Big[\frac{h}{3}+x_2\Big]=\frac{1}{\mu_3}\Big[\frac{h}{3}+\frac{h}{3}\Big(\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_2}+\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_1}\Big)\Big]\ [\because \mu_0=1\ \text{refractive index of air]}\)
\(=\frac{h}{3}\Big[\frac{1}{\mu_3}+\frac{1}{\mu_3}\Big(\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_2}+\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_1}\Big)\Big]\)
\(x_3=\frac{h}{3}\Big[\frac{1}{\mu_3}+\frac{\mu_3}{\mu_3}\Big(\frac{1}{\mu_2}+\frac{1}{\mu_1}\Big)\Big]=\frac{h}{3}\Big[\frac{1}{\mu_3}+\frac{1}{\mu_2}+\frac{1}{\mu_1}\Big]\)
\(\text{x}_3\) is apparent depth.


Sign Convention
Sign Convention
All measurements should be taken from pole of mirror. All measurements along the direction of incident ray will be positive and opposite to incident ray are negative. All the measurements for the distances above the principal axis are taken as positive and below the principal axis are taken as negative.For a real object, u is negative whereas v is negative for real image and positive for virtual image.


Phy Card 1
Reflection of Light
A light ray incident on the interface of two media is returned back into the same medium is called reflection of light.
► Laws of Reflection:
(i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
(ii) Incident ray, reflected ray and the normal lie in the same plane.
► Focal Length:
The distance between the pole and the principal focus is called focal length.


Phy Card 3
Mirror Equation
► Paraxial Rays:
These are the rays which are closer to the principal axis.
► Marginal Rays:
These are the rays which are far to the principal axis.
► Mirror Equation:
\(\frac{1}{Image\ distance\ (v)}\ +\ \frac{1}{Object\ distance\ (\mu)}\ =\ \frac{1}{focal\ length\ (f)}\)
\(\rightarrow\) The relation of between radius of curvature \(R\) and focal length \(f\) is \(R=2\ f\)


Phy Card 4
Snell's Law
► Linear Magnification
\(m\ =\ \frac{height\ of\ image\ (hi)}{{height\ of\ object\ (ho)}}\ =\ \frac{-\ v}{\mu}\)
► Refraction
The phenomenon of bending of light ray when it enters from one medium to another medium is called refraction.
► Laws of Refraction
(a) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
(b) Snell's Law:
\(M_{21}\ =\ \frac{sine\ of\ angle\ of\ incidence\ (\sin\ i)}{sine\ of\ angle\ of\ refraction\ (\sin\ r)}\)
Where \(M_{21}\) is the refractive index of second medium with respect to first medium


Phy Card 5
Critical Angle
► Optical Density:
It is the ratio of speed of light in two media. Refractive index \(\mu\) is a measure of optical density.
► Absolute Refractive Index:
\(\mu\ =\ \frac{C_{vaccum}}{C_{medium}}\ =\ \frac{speed\ of\ light\ in\ vaccum}{speed\ of\ light\ in\ medium}\)
► Critical Angle:
When a light ray travels from denser to rarer medium, then the angle of incidence for which the angle of refractions becomes \(90^\circ\) is called critical angle.


Phy Card 6
Total Internal Reflection
► When a ray of light travelling from denser to rarer medium such that the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, then the light is reflected totally into the denser medium. This phenomenon is called Total Internal Reflection (TIR).
(a) Mirages are due to TIR.
(b) Glittering of diamond is due to TIR.
(c) Optical fibre works on the principal of TIR.


Phy Card 7
Lens Formula
► Refraction at a spherical surface:
\(\frac{\mu_2}{v}\ -\ \frac{\mu_1}{u}\ =\ \frac{\mu_2\ -\ \mu_1}{R}\)
Where \(\mu_1\) is refractive index of the first medium and \(\mu_2\) is refractive index of second medium.
► Lens Maker's Formula;
(a) If \(R_1\ \ and \ \ R_2\) are radii of curvature, \(f\) is rhe focal length of a lens then \(\frac{1}{f}\ =\ (\mu\ -\ 1)\ \bigg(\frac{1}{R_1}\ -\ \frac{1}{R_2}\bigg),\) where \(\mu \) is the refractive index of material of lens.
(b) Lens Formula: If \(u\ \ and\ \ v\) are the object and image distances, \(f\) is the focal length of lens, then \(\frac{1}{f}\ =\ \frac{1}{v}\ -\ \frac{1}{u}\)


Phy Card 8
Power of Lens
► It is defined as the tangent of the angle by which it coverages or diverges a because of light falling at unit distance from the optical centre.
\(P\ =\ \frac{1}{f\ (in\ metres)}\ =\ \frac{100}{f\ (in\ cm)}\)
S.I Unit: Dipole (D)
► Power of a lens is positive for a converging lens and negative for a diverging lens.


Phy Card 9
Combination of Thin Lenses
(a) The number of thin lenses of focal lengths \(F_1,\ F_2,\ F_3,\ ...\ \) are in contact, if is the effective focal length, then
\(\frac{1}{f}\ =\ \frac{1}{f_1}\ +\ \frac{1}{f_2}\ +\ \frac{1}{f_3}\ +\ ...\)
(b) Equivalent Power
\(P\ =\ P_1\ +\ P_2\ +\ P_3\ +\ ...\)
(c) Effective Power
\(P\ =\ P_1\ +\ P_2\ -\ d\ (P_1\ P_2)\)


Phy Card 10
Refraction Through A Prism
(a) \(A\ =\ r_1\ +\ r_2\)
\( r_1\ \ and\ \ r_2\) are angles of refraction of a ray.
(b) \(\gamma\ =\ i_1\ +\ i_2\ -\ A\)
( Angle of deviation )
(c) Minimum deviation position
(i) \(r_1\ =\ r_2\ =\ r\ \ and\ \ i_1\ =\ i_2\ =\ i\)
(ii) \(A\ =2\ r\) (Angle of prism)
(iii) \(\gamma\ =\ Dm\ =\ 2\ i\ -\ A\) (Angle of deviation)
\(\mu_{21}\ =\ \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}\ =\ \frac{\sin\Big(\frac{A\ +\ Dm}{2}\Big)}{\sin\ (A/2)}\)
(iv) \(\gamma\ = \ (\mu\ -\ 1)\ A\ (angled\ prism).\)


 beeTokens
beeTokens