Electron in hydrogen atom first jumps from third excited state to second excited state and then from second excited to the first excited state. The ratio of the wavelength \(\lambda_1:\lambda_2\) emitted in the two cases is
(a) 7/5
(b) 27/20
(c) 27/5
(d) 20/7

The wave number (\(\bar v\)) of the radiation
\(=\frac{1}{\lambda}\)
\(=R_\infty \Bigl[\frac{1}{n^2_1}-\frac{1}{n^2_2}\Bigr]\)
Now for case \((\text I) \ n_1= 3, n_2 = 2 \)
\(\frac{1}{\lambda_1}=R_\infty\Bigl[\frac{1}{9}\frac{-1}{4}\Bigr],R_\infty=\text{ Rydberg constant } \)
\(\frac{1}{\lambda_1}=R_\infty\Bigl[\frac{4-9}{36}\Bigr]=\frac{-5R_\infty}{36}\)
\(\Rightarrow \lambda_1=\frac{-36}{5R_\infty} \)
\(\frac{1}{\lambda_2}=R_\infty\Bigl[\frac{1}{4}-\frac{1}{1}\Bigr]=\frac{-3R_\infty}{4}\Rightarrow \lambda_2=\frac{-4}{3R_\infty}\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{\lambda_1}{\lambda_2}=\frac{-36}{5R_\infty}\times \frac{3R_\infty}{-4}\Rightarrow \frac{\lambda_1}{\lambda_2}=\frac{27}{5}\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The force F acting on a particle of mass m indicated by force-time graph shown below.
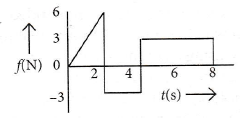
The change in momentum of the particle over the time interval from zero to 8 s is
(a) 24 Ns
(b) 20 Ns
(c) 12 Ns
(d) 6 Ns
Area under F-f curve will give change in momentum
\(\therefore\) According to the graph in question = Area = 12 Ns.
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Consider the following statements:
I. \(\lim\limits_{n\to\infty}\frac{2^n+(-2)^n}{2^n}\) does not exist
II. \(\lim\limits_{n\to\infty}\frac{3^n+(-3)^n}{4^n}\) does not exist
Then,
(a) I is true and II is false
(b) I is false and II is true
(c) I and II are true
(d) Neither I nor II is true
I. \(\lim\limits_{n\to\infty}\frac{2^n+(-2)^n}{2^n}=\lim\limits_{n\to\infty}1+(-1)^n=\) does not exist
II. \(\lim\limits_{n\to\infty}\frac{3^n+(-3)^n}{4^n}=\lim\limits_{n\to\infty}\Bigl(\frac{3}{4}\Bigr)^n+\Bigl(\frac{-3}{4}\Bigr)^n\)
\(=0+0=0\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
In the figure, galvanometer \(G\) gives maximum deflection when
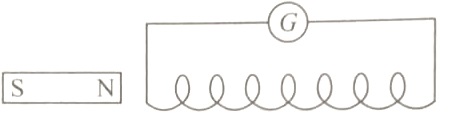
(a) magnet is pushed into the coil
(b) magnet is rotated into the coil
(c) magnet is stationary at the centre of the coil
(d) number of turns in the coil is reduced
When the magnet is pushed into the coil, magnetic flux linked with the coil changes. An emf is induced in the coil, which produces maximum deflection.
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The order of reactivity in nucleophilic substitution reaction is
(a) \(\text {CH}_3\text F\lt\text {CH}_3\text {Cl} \lt\text {CH}_3\text I\lt\text {CH}_3\text {Br} \) (b) \(\text {CH}_3\text F\lt\text {CH}_3\text {Cl} \lt\text {CH}_3\text {Br}\lt\text {CH}_3\text {I} \)
(c) \(\text {CH}_3\text F\lt\text {CH}_3\text {Br} \lt\text {CH}_3\text {Cl}\lt\text {CH}_3\text {I} \) (d) \(\text {CH}_3\text I\lt\text {CH}_3\text {Br} \lt\text {CH}_3\text {Cl}\lt\text {CH}_3\text {F} \)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
A circular loop of radius \(R\) carrying a current \(l\) is placed in a uniform magnetic field \(B\) perpendicular to the loop. The force on the loop is
(a) \(2\pi RI B\)
(b) \(2\pi R I^2 B^3\)
(c) \(\pi R^2IB\)
(d) zero
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
What are the zeroes of \(f(x)=8x^3-2x^2-3x\) ?
(a) \(\{ -\frac 1 2 \:,\frac 3 4\:\}\) (b) \(\{ -\frac 3 4\: ,\frac 1 2\:\}\)
(c) \(\{ -\frac 1 2\: ,\frac 1 2\: ,\frac 3 4\:\}\) (d) \(\{ -\frac 1 2\:,0\:,\frac 3 4\:\}\)
set the polynomial equal to zero and factor
\(8x^3-2x^2-3x=0\)
\(x(8x^2-2x-3)=0\)
\(x(2x+1)(4x-3)=0\)
\(x=0,x=-\frac 1 2,x=\frac 3 4\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
How many lines of symmetry does a rhombus have?
(a) 0 (b) 1
(c) 2 (d) 3
The line containing each diagonal of a rhombus is a line of symmetry .so a rhombus has 2 lines of symmetry
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The maximum number of possible interference maxima for slit-separation equal to twice the wavelength in young's double-slit experiment is ______
(a) infinite (b) five
(c) three (d) zero
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
\(\frac {(n!)^2} {[(n-1)!]^2}=\)
(a) \(2n\) (b) \(n\)
(c) \(n^2\) (d) \(n^4\)
\(\frac {(n!)^2} {[(n-1)!]^2}=\) \(\Big[\frac {(n!)} {[(n-1)!]}\Big]^2=n^2\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The maximum number of possible interference maxima for slit-separation equal to twice the wavelength in young's double-slit experiment is ______
(a) infinite (b) five
(c) three (d) zero
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
If \(\frac {n} {x^2-36}=\frac {1} {x-6} +\frac {1} {x+6}\) then n = _______
(a) \(x\) (b) \(2x\)
(c) \(2(x+6)\) (d) \(2(x-6)\)
multiply both sides of the equation by the LCD
\((x+6) (x-6)\)
\(n=(x+6)+(x-6)=2x\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
A body of mass m is accelerated uniformly from rest to a speed v in a time T. The instantaneous power delivered to the body as a function of time is given by _________
(a) \(\frac 1 2 \frac {mv^2} {T^2} t\) (b) \(\frac 1 2 \frac {mv^2} {T^2} t^2\)
(c) \( \frac {mv^2} {T^2} t\) (d) \(\frac {mv^2} {T^2} t^2\)
power = force \(\times\) velocity
\((ma) (v)=(ma) (at)=ma^2 t\)
(or) power= \(m \Big( \frac v T\Big) ^2 (t)= \) \( \frac {mv^2} {T^2} t\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
what is the sum of the infinite series?
\(1-\frac {1} {5}+\frac {1} {25}-\frac{1} {125}+...........?\)
(a) \(\frac 5 6\) (b) \(\frac 1 5\)
(c) \(\frac 6 5\) (d) \(-\frac {5} {6}\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The solution of the differential equation \(y\:dx+(x+x^2y)\:dy=0\) is ______
(a) \(\log y =Cx\) (b) \(-\frac {1} {xy}+\log y=C\)
(c) \(\frac {1} {xy}+\log y=C\) (d) \(-\frac {1} {xy}=C\)
we have
\(y\:dx+(x+x^2y)\:dy=0\)
\(y \:dx+x\:dy+x^2y\:dy=0\)
\(\frac {d(xy)} {(xy)^2}+\frac {1} {y}dy\)
{ dividing throughout by \((xy)^2\) }
On Integrating, we get
\(-\frac {1} {xy}+\log y=C\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The solution of the Differential equation \(\frac {dy} {dx}=\frac {x+y} {x}\) satisfying the condition \(y(1)=1\) is ______
(a) \(y=x \ln x+x\)
(b) \(y= \ln x+x\)
(c) \(y=x \ln x+x^2\)
(d) \(y=x\: e^{(x-1)}\)
\(\frac {dy} {dx}=\frac {x+y} {x}\)
\(x \:dy-y \: dx=x\: dx\)
\(\frac { x\: dy-y\:dx} {x^2}=\frac {dx} {x}\)
\(d\Big(\frac {y} {x}\Big)=\frac {dx} {x}\)
\(y=x\ln x +kx\)
k=1
\(y=x \ln x+x\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Two lenses of power -15 D and +5D are in contact with each other. The focal length of the combination is ____
(a) +10 cm (b) -20 cm
(c) -10cm (d) + 20 cm
Power of combination = \(P_1+P_2\)
\(=-15D+5D=-10 D\)
Focal Length of combination F
\(=\frac {1} {p}= \frac {1} {-10 D}=-0.1 \:m=-10\:cm\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
If the roots of the quadratic equation \(x^2+px+q=0\) are \(\tan 30^0\) and \(\tan 15^0\) respectively then the value of \(2+q-p\) is _____
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 0 (d) 1
\(\alpha=\tan 30^0\)
\(\beta =\tan 15^0\)
\(x^2+px+q=0\)
\(\alpha+\beta=-p\) and \(\alpha.\beta=q\)
using \(\tan A+\tan B=\tan (A+B).(1-\tan A.\tan B)\)
\(-p=1-q\)
\(q-p=1\)
\(2+q-p=3\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The function \(f(x)= \frac {x} {1-2^x}-\frac {x} {2}\) is _____
(a) An even but not odd function
(b) An odd but not even function
(c) A both even and odd function
(d) A neither even nor odd function
\(f(-x)=\frac {-x} {1-2^{-x}} - \frac {-x} {2}\)
\(=\frac {-x.2^x} {2^x-1} +\frac {x} {2}\)
\(=\frac {x} {1-2^x}-x+\frac {x} {2}\)
\(=\frac {x} {1-2^x} -\frac {x} {2}=f(x)\)
\(f(-x)=f(x)\)
f(x) is an even function
Obviously not odd function
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
A wheel whose moment of inertia is \(12kg\:m^2\) has an initial angular velocity of 40 rad/s.A constant torque of 20 Nm acts on the wheel. The time in which the wheel is accelerated to 100 rad/s is _____
(a) 72 second (b) 16 second
(c) 8 second (d) 36 second
Formula : \(\alpha =\frac {\tau } {I}\)
\(\alpha =\frac {20 N.m} {12 kg \:m^2}=\frac {20} {12} rad \:s^{-2}\)
\(\omega =\omega_0+\alpha t\)
\(100=40+\big(\frac {20} {12}\Big) t\)
\(t=\frac {(100-40)\times 12} {20}=365\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
If \(\displaystyle\int_{0}^{\pi} x f(\sin x ) \: dx=A\int_{0}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} f(\sin x) \: dx\) then A is ____
(a) \(\frac {\pi} {4}\) (b) \(\pi\)
(c) 0 (d) \(2\pi\)
\(\int_{0}^{\pi} x f(\sin x ) \: dx=A\int_{0}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} f(\sin x) \: dx\)
or \(A\int_{0}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} f(\sin x)\: dx =\frac {\pi} {2} \int_{0}^{\pi} f(\sin x) \;dx=\int_{0}^{\pi} f(\sin x) dx\)
\(A\int_{0}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} f(\sin x)\: dx =\frac {\pi} {2} \times 2\int_{0}^{\frac {\pi} {2}}f(\sin x) \;dx\)
\(A\int_{0}^{\frac {\pi} {2}} f(\sin x)\: dx = {\pi} \int_{0}^{\frac {\pi} {2}}f(\sin x) \;dx\)
\(A=\pi\) using properties of integrals
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Let \(f(x)=(x+|x|) |x|\) then, for all x
(a) \(f\) is continuous
(b) \(f\) is differentiable for some x
(c) \(f^{'}\) is continuous
(d) \(f^{''}\) is continuous
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Let \(\epsilon_0\) denote the dimenstional formula of the permittivity of vacuum .If M=mass,L= length ,T=time and A= electric current ,then ___________
(a) \([\epsilon_0]=[M^{-1} L^2 T^{-1} A]\)
(b) \([\epsilon_0]=[M^{-1} L^{-3} T^{2} A]\)
(c) \([\epsilon_0]=[M^{-1} L^{-3} T^{4} A^2]\)
(d) \([\epsilon_0]=[M^{-1} L^2 T^{-1} A^{-2}]\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
\(x-5y=2\) and \(3x+y=6\) , \((xy)^2\) = ______
(a) 0 (b) 1
(c) 4 (d) 9
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
\(\displaystyle\lim_{n\to\infty}\bigg[\frac{1}{1\cdot2}+\frac{1}{2\cdot3}+\frac{1}{3\cdot4}+...+\frac{1}{n(n+1)}\bigg]\) is equal to
(a) 1 (b) - 1
(c) 0 (d) None of these
\(\displaystyle\lim_{n\to\infty}\bigg[\frac{1}{1\cdot2}+\frac{1}{2\cdot3}+\frac{1}{3\cdot4}+...+\frac{1}{n(n+1)}\bigg]\)
\(=\displaystyle\lim_{n\to\infty}\bigg[\bigg(1-\frac{1}{2}\bigg)+\bigg(\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{3}\bigg)+\bigg(\frac{1}{3}-\frac{1}{4}\bigg)+.....+\bigg(\frac{1}{n}-\frac{1}{n+1}\bigg)\bigg]\)
\(=\displaystyle\lim_{n\to\infty}\bigg(1-\frac{1}{n+1}\bigg)=\displaystyle\lim_{n\to\infty}\frac{n}{n+1}\)
\(=\displaystyle\lim_{n\to\infty}\frac{n}{n\bigg(1+\frac{1}{n}\bigg)}=\displaystyle\lim_{n\to\infty}\frac{1}{\bigg(1+\frac{1}{n}\bigg)}=1\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The electric potential at any point is \(V=-5x+3y+\sqrt{15z},\) then the magnitude of the electric field is
(a) \(3\sqrt 2\)
(b) \(4\sqrt 2\)
(c) \(5\sqrt 2\)
(d) \(7\)
\(E_x=-\frac{rv}{rx}=\frac{-r}{rx}(-5x+5y+\sqrt{15z})=5\)
\(E_y=\frac{rv}{ry}=-3,E_z=-\sqrt{15}\)
Now, \(E=\sqrt{E^x_y+E^z_y+E^z_z}=7\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
sodium and copper have work functions 2.3eV and 4.5 eV respectively. Then the ratio of the wavelengths of sodium compared to copper is nearest to ________
(a) 1:2 (b) 4:1
(c) 2:1 (c) 1:4
work function = \(\frac {hc} {\lambda}\)
\(\frac {W_{Na}} {W_{cu}}=\frac {4.5} {2.3}=\frac {2 } {1}\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
The velocity of a particle is \(v=v_0+gt+ft^2\) .If its position is \(x=0\) at \(t=0\) then its displacement after unit time \((t=1)\) is ________
(a) \(v_0+\frac {g} {2} +f\) (b) \(v_0+2g+3f\)
(c) \(v_0+\frac {g} {2} +\frac f 2\) (d) \(v_0+g+f\)
Given: Velocity
\(v=v_0+gt+ft^2\)
\(v=\frac {dx} {dt}\) (or) \(\displaystyle\int_{0}^{x}dx=\int_{0}^{t} v dt\)
\(x=\int_{0}^{t}(v_0+gt+ft^2) dt\)
\(x=v_0t+\frac{gt^2} {2}+\frac {ft^3} {3}+C\)
\(x=0,t=0
\)
\(c=0\) (or) \(x=v_0t+\frac{gt^2} {2}+\frac {ft^3} {3}\)
at t=1 sec
x = \(v_0+\frac {g} {2} +\frac f 2\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
Six identical coins are arranged in a row, the number of ways in which the number of trials is equal to the number of heads is _____
(a) 9 (b) 20
(c) 40 (d) 120
The required number of ways in which letters HHHTTT can be arranged
Hence they can be altogether arranged is 6! ways but we have to count for 3 respective heads and tials the required permutation is
\(=\frac {6!} {3! 3!}=\frac {6\times 5 \times 4} {3!}=20\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated
If \(f(x)=\frac {(3x+2)}{ (5x-3)} \) then _____
(a) \(f^{-1} (x)=-f(x)\)
(b) \(f^{-1} (x)=f(x)\)
(c) \(fo (f(x))=-x\)
(d) \(f^{-1} (x)=-\frac {1} {19}\:f(x)\)
Let \(y=\frac {(3x+2)}{ (5x-3)} =f(x)\)
\(y(5x-3)=3x+2\)
\(x=\frac {3y+2} {5y-3}\)
\(f^{-1}(y)=\frac {3y+2} {5y-3}\)
\(f^{-1} (x)=\frac {(3x+2)}{ (5x-3)} =f(x)\)
Topic image not updated
More information not updated