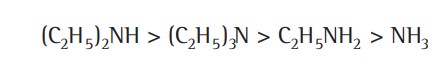Common Uses Of Amines
- In nature, amines occur among proteins, vitamins, alkaloids and hormones.
- Synthetic examples include polymers, dye stuffs and drugs.
- Biologically active compounds, namely adrenaline and ephedrine, both containing a secondary amino group, are used to increase blood pressure.
- Novocain, a synthetic amino compound, is used as an anaesthetic in dentistry.
- Benadryl, a well known antihistaminic drug also contains tertiary amino group.
- Quaternary ammonium salts are used as surfactants.
- Diazonium salts are intermediates in the preparation of a variety of aromatic compounds, including dyes.


Characteristics Of Amines
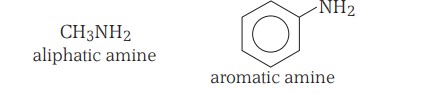
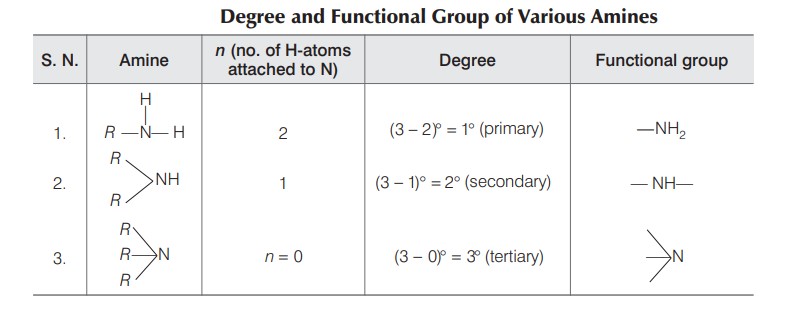
Aliphatic and aromatic amines are alkyl and aryl derivatives of ammonia in which one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia have been replaced by alkyl and aryl groups, respectively. For example,


Structure Of Amines
Nitrogen atom possesses four sp3 hybridised orbitals. In amines, out of these four, three sp3 hybridised orbitals overlap either with the sp3 hybridised orbitals of the —CH3 group (alkyl group) or with the s orbital of the —H atom or with both to form three (σ) bonds.
The remaining fourth sp3 hybridised orbital, being completely filled, does not take part in bond formation. Here, it is obvious that there are three (σ) bonds and one lone pair over nitrogen in amines.
Thus, all amines, i.e., 1°, 2° and 3°, have pyramidal geometry.
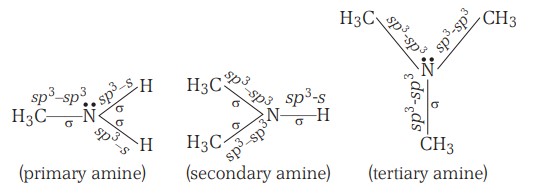


Preparation - Reduction Of Nitro Compounds
Nitro compounds are reduced to amines by passing hydrogen gas in the presence of finely divided nickel, palladium or platinum and also by reduction with metals in acidic medium.
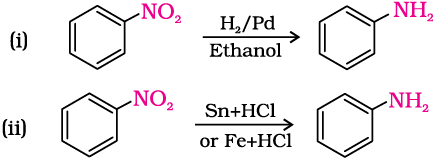
Reduction with iron scrap and hydrochloric acid is preferred because FeCl2 formed gets hydrolysed to release hydrochloric acid during the reaction. (Only a small amount of hydrochloric acid is required to initiate the reaction.)


Preparation - Ammonolysis Of Alkyl Halides
When an alkyl halide is heated with an alcoholic solution of ammonia in a sealed tube at about 393 K, a mixture of amines is obtained. This reaction is called Hofmann’s ammonolysis method.
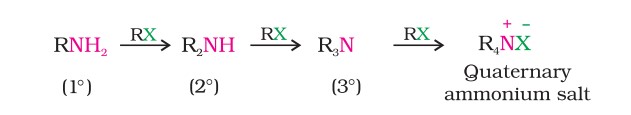
This reaction follows the SN2 mechanism. Primary amine is the main product if an excess of ammonia is used.
The order of reactivity of halides with amines is RI > RBr >RCl.


Preparation - Reduction Of Nitriles And Amides
- Nitriles, on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride or catalytic hydrogenation, produce primary amines. This reaction is used for the ascent of the amine series, i.e., for the preparation of amines containing one carbon atom more than the starting amine.
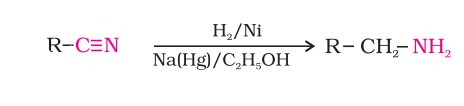
- The amides, on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride, yield amines.
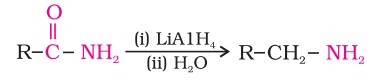


Preparation - Gabriel Pthalimide Synthesis
This method is used for the preparation of primary amines. Phthalimide, on treatment with ethanolic KOH, forms the potassium salt of phthalimide, which, on heating with alkyl halide followed by alkaline hydrolysis, produces the corresponding primary amine.
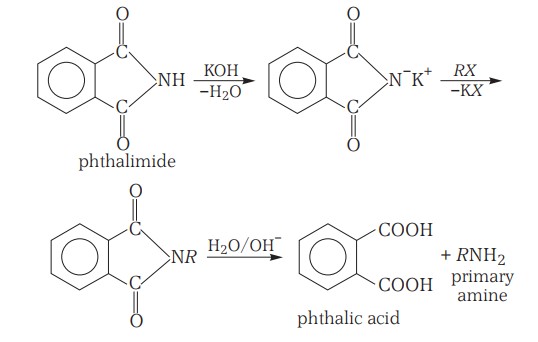
Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared by this method because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by phthalimide.


Preparation - Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation
Hoffmann developed a method for the preparation of primary amines by treating an amide with bromine in an aqueous or ethanolic solution of sodium hydroxide.
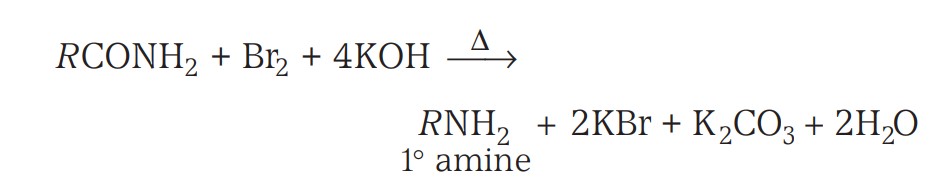
The amine so formed contains one carbon less than that present in the amide.


Physical Properties Of Amines
1. Lower amines are gases or low-boiling liquids, with a characteristic ammonia-like smell.
2. Their boiling point are higher in comparison to non-polar compounds of the same molecular weight (due to intermolecular H-bonding). However, tertiary amines are exceptions of this due to absence of H-bonding.
The order of boiling points of isomeric amines is - Primary > Secondary > Tertiary
3. These are miscible with water (due to intermolecular H-bonding with water molecules also).



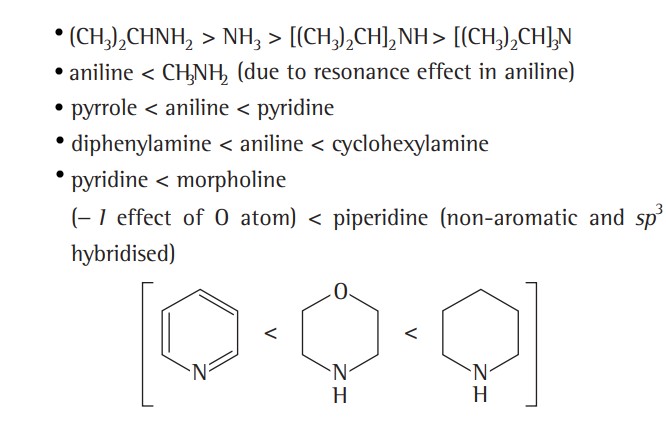
Basicity In Amines
All amines are basic due to the presence of a lone pair of electrons for protonation. Their basicity, i.e., availability of lone pair for protonation, is affected by the following three factors -
(i) Alkyl group substitution (They have +I effect, thus as their number increases, the electron density over nitrogen increases. Hence, the lone pair will become more available for protonation, resulting in increased basicity.)
(ii) Steric effect (The Greater the number of methyl groups, the lesser will be the basic strength.)
(iii) Solvation effect (The greater the solvation of cation, more will be the tendency of amine to change to cation by releasing the electron pair on the nitrogen atom. Thus, more will be the basic strength of the amine.)


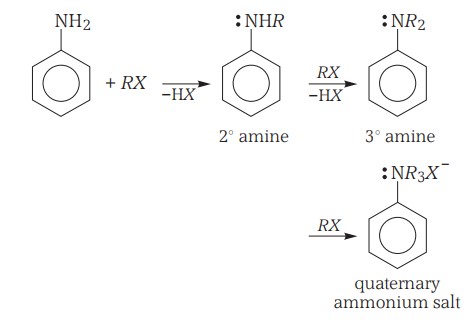
Chemical Reactions - Alkylation
Primary aliphatic amines and aromatic amines react with alkyl halides to give respective secondary and tertiary amines.
An example of the reaction is as follows -


Chemical Reactions - Acylation
Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines react with acid chlorides, anhydrides and esters by nucleophilic substitution reaction (Acylation). You can consider this reaction as the replacement of the hydrogen atom of –NH2 or >N–H group by the acyl group. The products obtained are known as amides. The reaction is carried out in the presence of a base, like pyridine, which removes HCl so formed and shifts the equilibrium to the right-hand side.
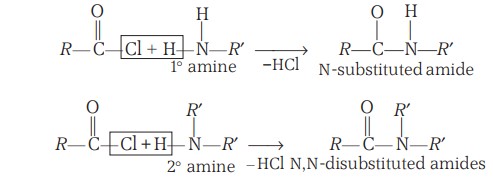
Amines also react with benzoyl chloride (Benzoylation).
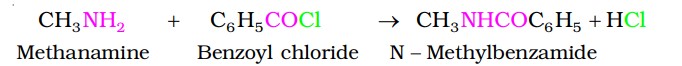


Chemical Reactions - Carbylamine
Aliphatic and aromatic primary amines, on heating with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide, form isocyanides or carbylamines, which are foul-smelling substances. Secondary and tertiary amines do not show this reaction.

This reaction is known as the carbylamine reaction or isocyanide test and is used as a test for primary amines.


Chemical Reactions - With Nitrous Acid
(a) Primary aliphatic amines react with nitrous acid to form aliphatic diazonium salts, which, being unstable, liberate nitrogen gas quantitatively and alcohols.
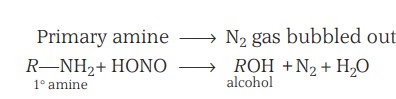
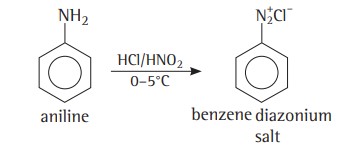
(b) Aromatic amines react with nitrous acid at low temperatures (273-278 K) to form diazonium salts, a very important class of compounds used for the synthesis of a variety of aromatic compounds.


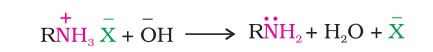
Chemical Reactions - Hinsberg Reagent
Hinsberg reagent (arylsulphonyl chloride) is used to distinguish between 1°, 2° and 3° amines.
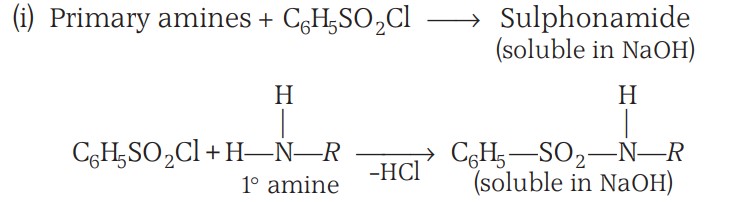
The hydrogen attached to nitrogen in sulphonamide is strongly acidic due to the presence of a strong electron-withdrawing sulphonyl group. Hence, it is soluble in alkali.
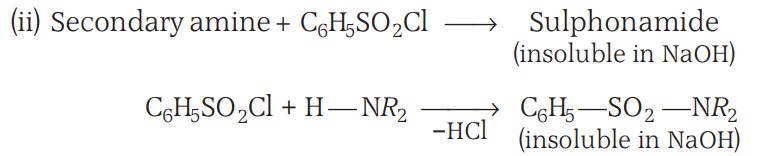
Since N, N-diethylbenzene sulphonamide does not contain any hydrogen atom attached to the nitrogen atom, it is not acidic and hence insoluble in alkali.
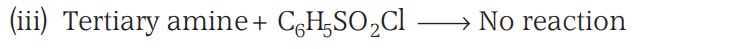


Electrophilic Substitution - Bromination
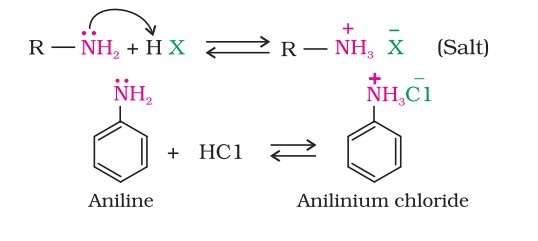
Aniline reacts with bromine water at room temperature to give a white precipitate of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline.
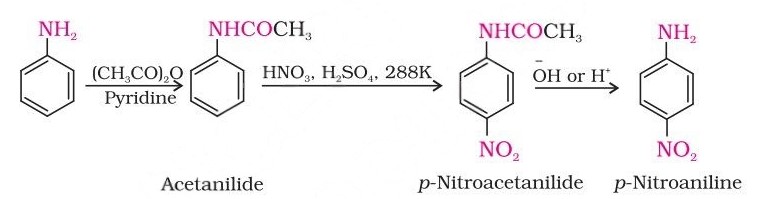
To prepare a monosubstituted aniline derivative, the activating effect of the –NH2 group must be controlled by protecting the -NH2 group through acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution, followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.
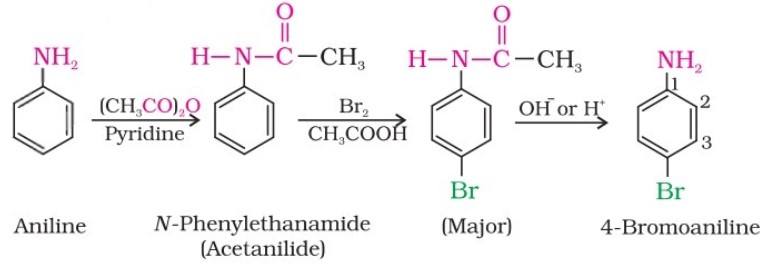


Electrophilic Substitution - Nitration
Direct nitration of aniline yields tarry oxidation products in addition to the nitro derivatives. Moreover, in the strongly acidic medium, aniline is protonated to form the anilinium ion, which is meta-directing.
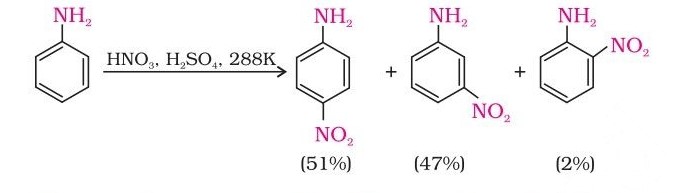
However, by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation reaction with acetic anhydride, the nitration reaction can be controlled, and the p-nitro derivative can be obtained as the major product.


Electrophilic Substitution - Sulphonation
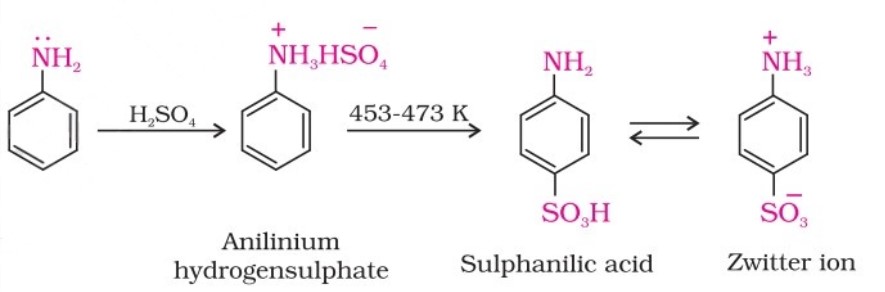
Aniline reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid to form anilinium hydrogen sulfate, which, upon heating with sulfuric acid at 453-473 K, produces p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid, commonly known as sulphanilic acid.


Diazonium Salts - Preparation And Physical Properties
Benzenediazonium chloride is prepared by the reaction of aniline with nitrous acid at 273- 278 K.
Nitrous acid is produced in the reaction mixture by the reaction of sodium nitrite with hydrochloric acid. The conversion of primary aromatic amines into diazonium salts is known as diazotisation. Due to its instability, the diazonium salt is not generally stored and is used immediately after its preparation.
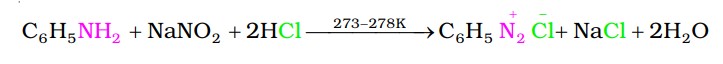
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES -
- Benzenediazonium chloride is a colourless crystalline solid. It is readily soluble in water and is stable in cold temperatures, but it reacts with water when warmed. It decomposes easily in the dry state.
- Benzenediazonium fluoroborate is water-insoluble and stable at room temperature.


Gatterman Reaction
Chlorine or bromine can also be introduced in the benzene ring by treating the diazonium salt solution with the corresponding halogen acid in the presence of copper powder. This is referred to as the Gatterman reaction.

However, the yield in the Sandmeyer reaction is found to be better than the Gattermann reaction.


Replacement By Iodide And Fluoride Ion
Replacement by Iodide ion: Iodine is not easily introduced into the benzene ring directly, but, when the diazonium salt solution is treated with potassium iodide, iodobenzene is formed.

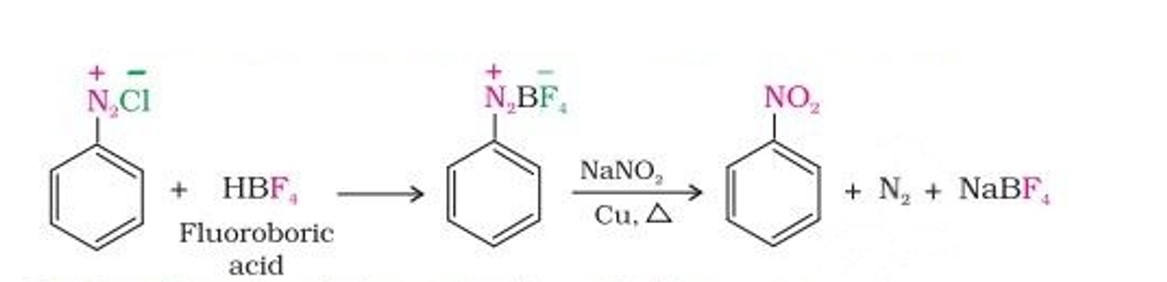
Replacement by Fluoride ion: When arenediazonium chloride is treated with fluoroboric acid, arene diazonium fluoroborate is precipitated which on heating decomposes to yield aryl fluoride.



Replacement By H And Hydroxyl Group
Replacement by H: Certain mild reducing agents like hypophosphorous acid (phosphinic acid) or ethanol reduce diazonium salts to arenes and themselves get oxidised to phosphorus acid and ethanal, respectively.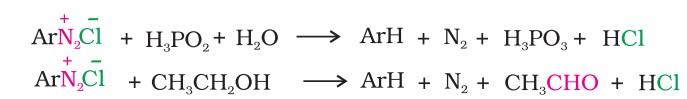
Replacement by hydroxyl group: If the temperature of the diazonium salt solution is allowed to rise up to 283 K, the salt gets hydrolysed to phenol.
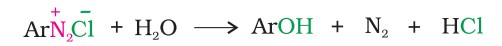


Replacement By Nitrite Group
Replacement by nitrite group: When diazonium fluoroborate is heated with aqueous sodium nitrite solution in the presence of copper, the diazonium group is replaced by the –NO2 group.


Coupling Reactions
The azo products obtained have an extended conjugate system having both aromatic rings joined through the –N=N– bond. These compounds are often coloured and are used as dyes.
Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol, in which the phenol molecule at its para position is coupled with the diazonium salt to form p-hydroxyazobenzene. This type of reaction is known as a coupling reaction. Similarly, the reaction of diazonium salt with aniline yields p-aminoazobenzene.
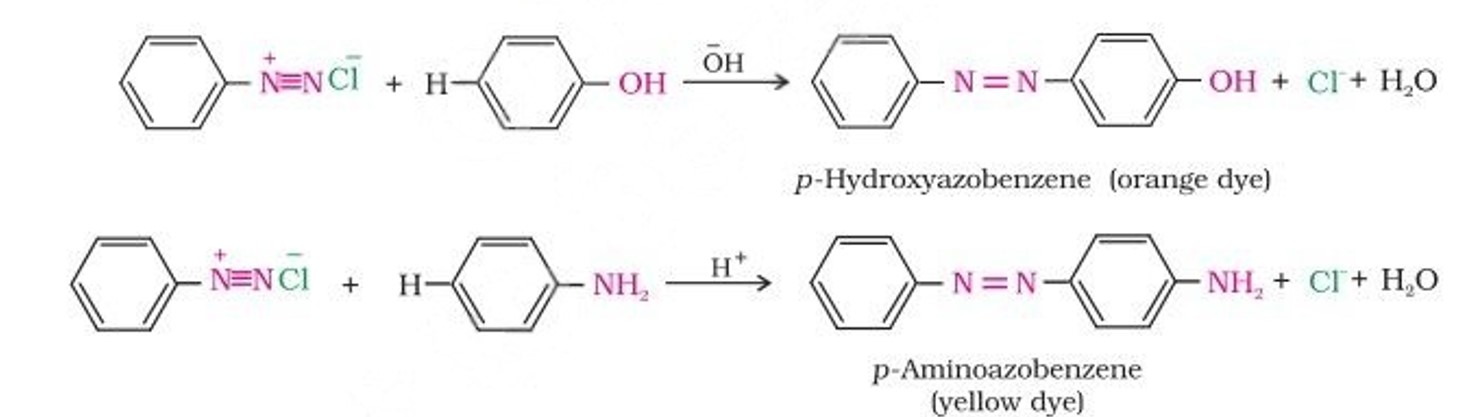
They are examples of electrophilic substitution reactions.


 beeTokens
beeTokens